Lithium vanadium phosphate LVP
C 5%-Li3V2( PO4 )3
Carbon coated lithium vanadium phosphate (5%C-LVP) lithium battery anode material, strong ionic conductivity, high capacity, high voltage platform, good safety.
Need to customized production.
- 描述
- Inquiry
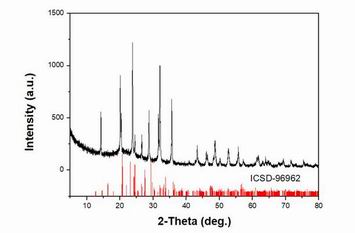
Lithium vanadium phosphate is a kind of polyanionic anode material, which has the advantages of good stability, high safety, high theoretical capacity, high operating voltage and low price.
Lithium vanadium phosphate is a monoclinic structure compound with a higher positive lithium ion diffusion system and a higher discharge voltage (3.6/4.1V). At the same time, due to the addition of carbon in the lithium vanadium phosphate complex, the overall energy density and safety are high, which can not only exclude the shortcomings of lithium cobalt acid and lithium iron phosphate, but also improve the electrical conductivity [1]. However, vanadium material has the disadvantages of difficult extraction of precursor, high energy loss and high toxicity, so it is very important to analyze the application of graphene in the preparation of lithium vanadium phosphate for lithium ion batteries.
Lithium vanadium phosphate cationic and anion doping
On the one hand, the lithium vanadium phosphate/graphene complex crystal is a three-dimensional framework, which mainly includes phosphate tetrahedron and octahedron. Since lithium ions can be freely diffused within the crystal during the charge and discharge process, in order to ensure the electrochemical performance of lithium vanadium phosphate/graphene, the lithium ion diffusion channel in lithium vanadium phosphate materials can be further expanded by adjusting the number of cations or anions of lithium vanadium phosphate/graphene. The commonly used lithium vanadium phosphate/graphene modified cations are mainly manganese ions, barium ions, chromium ions and antimony ions. Taking chromium ion doping modification as an example, lithium carbonate, chromium acetate, ammonium hydrogen phosphate and ammonium metavanadate can be weighed according to the measurement ratio of house type in previous experiments. The mixture is then incorporated into 80mL of deionized water and the acid saturated solution is gradually added. After full stirring, adjust the pH to 7.0 with ammonia. The mixture was then placed in a water bath heated stirring instrument (80°C/3.5h) and an oven (80°C/10h). The modified material is cooled to room temperature in argon and then ground. By adjusting the proportion of chromium acetate, it can be concluded that with the increase of the proportion of chromium acetate, the diffraction peak crystal plane spacing of lithium vanadium phosphate material increases gradually, indicating that the material modification is successful. On the other hand, in the anionic doping of lithium vanadium phosphate/graphene, the main doped materials are chloride ions, fluorine ions and boric acid ions. Taking the addition of chloride ions as an example, the materials of lithium chloride, ammonium hydrogen phosphate, lithium carbonate and ammonium metavanadate can be classified according to the stoichiometric ratio.
相关产品
-
Rubidium chromate
Other name: dirubidium dioxido(dioxo)chromium
CAS Number: 13446-72-5
EINECS number: 236-601-1
Molecular formula: CrO4Rb2
Molecular Weight: 286.9293
Density: 3.518
Appearance: Yellow crystal powder
Chemical properties: Soluble in water, its aqueous solution is alkaline.
-
Sodium pyroantimonate
CAS no. : 12507-68-5
Molecular formula: NaSb(OH)6
Molecular weight: 246.787
-
Rubidium fluoride
Other name: Rubidium monofluoride
CAS no. : 13446-74-7
EINECS no. : 236-603-2
Molecular formula: FRb
Molecular weight: 104.4662
Melting point (℃) : 775.
The boiling point (℃) : 1410.
Relative density (water =1) : 3.56.
The saturation vapor pressure (kPa) : 0.13 (920 ℃).
Solubility: soluble in water, insoluble in ethanol, ether, liquid ammonia, soluble in hydrofluoric acid.
-
Caesium fluoride
Other name: Cesium fluoride
CAS no. : 13400-13-0
EINECS no. : 236-487-3
Molecular formula: CsF
Molecular weight: 151.9039
Melting point: 682℃
Boiling point: 19.5 ° C at 760 mmHg
Solubility in water: 369 g / 100 mL (18℃)
The vapor pressure, 922 MMHG at 25°C
-
Sodium hexafluoroantimonate
Other name: Sodium hexafluoroantimonate(V); ; 1,4-dibromo-2-chloro-1,1-difluorobutane; sodium antimony hexafluoride; sodium hexafluoroantimonate(1-)
CAS Number: 16925-25-0
EINECS number: 240-989-8
Molecular formula: F6NaSb
Molecular weight: 258.7402
-
dipotassium trioxotellurate powder
Other name: Potassium tellurate(IV); POTASSIUM TELLURITE; dipotassiumtrioxotellurate; telluricacid(h2teo3),dipotassiumsalt; Tellurousacid,dipotassiumsalt; dipotassium tellurite.
CAS number: 7790-58-1
EINECS number: 232-213-1
Molecular formula: K2O4Te
Molecular weight: 269.7942
Density (g / mL, 25 ° C): 3.503
Melting point (oC): 460-470
-
Cesium tungstate
English alias: Cesium tungsten oxide (Cs2WO4); Cesium tungstate. Dicesium tungsten tetraoxide; Dicesium; Oxygen anion (2); Tungsten; Dicaesium dioxido (dioxo) tungsten
CAS no. : 13587-19-4
EINECS no. : 237-019-0
Molecular formula: Cs2O4W
Molecular weight: 513.6485
-
Potassium Silicate Titanate
Name: Potassium Silicate Titanate
Other name: Fused Potassium Silico-Titanate
-
Cesium iodide
Other name: caesium iodide
CAS no. : 7789-17-5
EINECS no. : 232-145-2
Molecular formula: CsI
Molecular weight: 259.8099
Melting point: 626 ℃
Boiling point: 127 ° C at 760 mmHg
Solubility in water: 74 g / 100 mL (20 ℃)
Vapor pressure: 13.8 mmHg at 25 ° C
-
Aluminum lithium tetrachloride
Other name: Lithium Aluminum Tetrachloride; Lithium tetrachloroaluminate; lithium tetrachloroaluminum; Lithium chloroaluminate (6CI); Aluminum lithium chloride (AlLiCl4)
CAS no. : 14024-11-4
EINECS no. : 237-850-9
Formula: LiAlCl4
Molecular weight: 175.7345
Chemical properties: Water or moisture absorption decomposition
Appearance: White or off-white powder