Molybdenum Carbide powder
English alias: Molybdenum carbide (Ⅳ); Methane – molybdenum (1:1)
CAS no. : 12627-57-5; 12011-97-1
EINECS no. : 235-733-7
Molecular formula: CH4Mo.
Molecular weight: 111.9825
Density: 9.18g / cm3
Melting point: 2690 °C
- 描述
- Main use
- Inquiry
Colour: Dark gray
Crystal form: Six parties
Thermal expansion coefficient: 7.8 × 10 -6 / K
Thermal conductivity: 6.54W / m.K
Moh’s hardness: 7
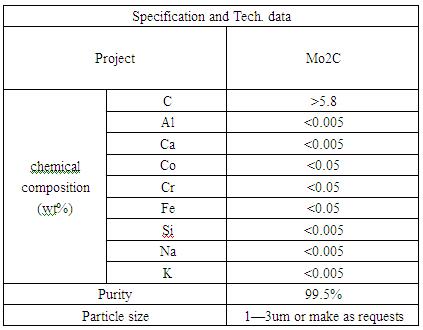
The basic characteristics of molybdenum carbide powder:
Molybdenum carbide is a dark gray metallic powder containing 5.89% (theoretical combined amount) of carbon whose crystals are packed hexagonal lattices. As a class of new functional materials with high melting point and hardness, good thermal and mechanical stability, and excellent corrosion resistance, they have been widely used in various fields such as high temperature resistance, abrasion resistance and chemical corrosion resistance.
Molybdenum carbide has similar electronic structure and catalytic properties as noble metal, especially its hydrogenation activity is equivalent to that of Pt, Pd and other noble metals. It is expected to become a substitute for noble metal and can be widely used in reactions involving hydrogen such as paraffin isomerization, Unsaturated hydrocarbon hydrogenation, hydrodesulfurization and denitrification reaction catalyst.
Molybdenum carbide high hardness, abrasion resistance, abrasion resistance. It is an important component of molybdenum-molybdenum carbide hard coatings and other cermet coatings and can also be used alone as a wear-resistant, scratch-resistant coating.
Molybdenum carbide does not react with anaerobic acid; it dissolves in nitric acid and aqua regia; reacts with chlorine only at high temperatures; it works with fluorine at room temperature; molybdenum oxide is formed when heated in the air.
Molybdenum carbide for material modification
Mo carbide used in the field of material modification, mainly because of its high melting point and hardness, good thermal and mechanical stability, excellent corrosion resistance characteristics. It can be used as a coating material, can also be used as an additive material.
Molybdenum carbide is often used as a coating material for some areas of high hardness, abrasion resistance and high temperature resistance. Molybdenum carbide (MoC) and tungsten carbide are mixed, the appropriate lanthanum powder is added, sintered into a hard material, coarsely pulverized and then added with a certain amount of nickel, and the usual cemented carbide production method is used to obtain a well-distributed binder phase And refined molybdenum carbide-based cemented carbide. Molybdenum carbide can also be added to cermets to improve their properties. In addition, molybdenum carbide is also commonly used in particle reinforced alloys.
Molybdenum carbide is used as a catalytic material
Molybdenum carbide has some properties of noble metal, which can be comparable to noble metal platinum and iridium for hydrocarbon dehydrogenation, catalytic activity of hydrogenolysis and isomerization reaction, and is praised as "quasi-platinum catalyst". In particular, its price is cheaper than the expensive metal and has excellent anti-sulfur poisoning performance, making it in the catalyst field has a broad application prospects. As an excellent catalytic material, molybdenum carbide must have a high specific surface area.
相关产品
-
Ammonium niobium oxalate
English alias: Ethanedioic acid ammonium niobium (5 +) salt , Ammonium niobate (v) oxalate hydrate
CAS no. : 168547-43-1
Molecular formula: C4H4NNbO9
Molecular weight: 302.98 g / mol
-
Niobium boride
Other name : niobiumbago (NBB); boranylidyneniobium
CAS no. : 12653-77-9; 12045-19-1
EINECS no. : 234-958-8
Formula: B2Nb.
Molecular weight: 103.7174.
Density: 7g/cm3
Melting point: 3050℃
-
Tantalum nitride
Performance characteristics: high purity, no impurity phase detected by XRD
Tantalum nitride (TaN) has superior physical, chemical and mechanical properties (such as high hardness, wear resistance, chemical inertness, thermal stability and low resistance temperature coefficient), and is widely used in wear-resistant coatings, film resistors and diffusion barriers in integrated circuits -
Nano vanadium dioxide VO2
Other name: Vanadium oxide; Dioxovanadium
Appearance: black powder
Grain size: 50nm, 100nm, 500nm
Purity: 99.9%, 98% ( tungsten mingle ) -
Niobium metaphosphate
English name: Niobium metaphosphate
Chemical formula: Nb (PO3) 5
Molecular weight: 487.90
Properties: sodium biphosphate glass, white powder, insoluble in water, PH value: 3.8
-
Tungsten silicide
Other name: Tungsten disilicide
CAS no. : 12039-88-2
EINECS no. : 234-909-0
Formula: Si2W.
Molecular weight: 240.011
Density: 9.40 g/cm3
Melting point: 2165 C.
-
Titanium black Ti4O7
Blue Black electrically conductive powder
Produced by proprietary process
High Ti407 Content
Structurally Stabilized Sheer Planes
High Resistance to oxidation and corrosion
in acid and base solutionsStabilized Magneli Phase Titanium Oxide
Electrically Conductive Ceramic PowderD50 particle size: 80nm, 20um
-
Zirconium tungstate
Other name:
Tungsten zirconium oxide ; Ditungsten zirconium octaoxide
CAS no. : 16853-74-0
EINECS no. : 240-876-3
Molecular formula: Zr(WO4)2
Molecular weight: 586.8992.
-
Niobium hydroxide
Specification: 99.9%, 99.99%
Other name: Niobium hydroxide oxide
CAS no. : 37349-30-7
Molecular formula: Nb(OH)5Mainly used in catalyst, new energy and other new industry production.
-
Vanadate zirconium
Molecular formula: ZrV2O7.
Molecular weight: 315.7.
CAS no. : 13981-20-9
Appearance: yellow powder
Used in functional ceramics, structural ceramics and other aspects as pigments.
Description: The use of temperature: 400-1080 ℃
The coefficient of linear expansion: – 10 x 10-6 ℃ – 1